Long-‐life supplementation with atenolol…
261
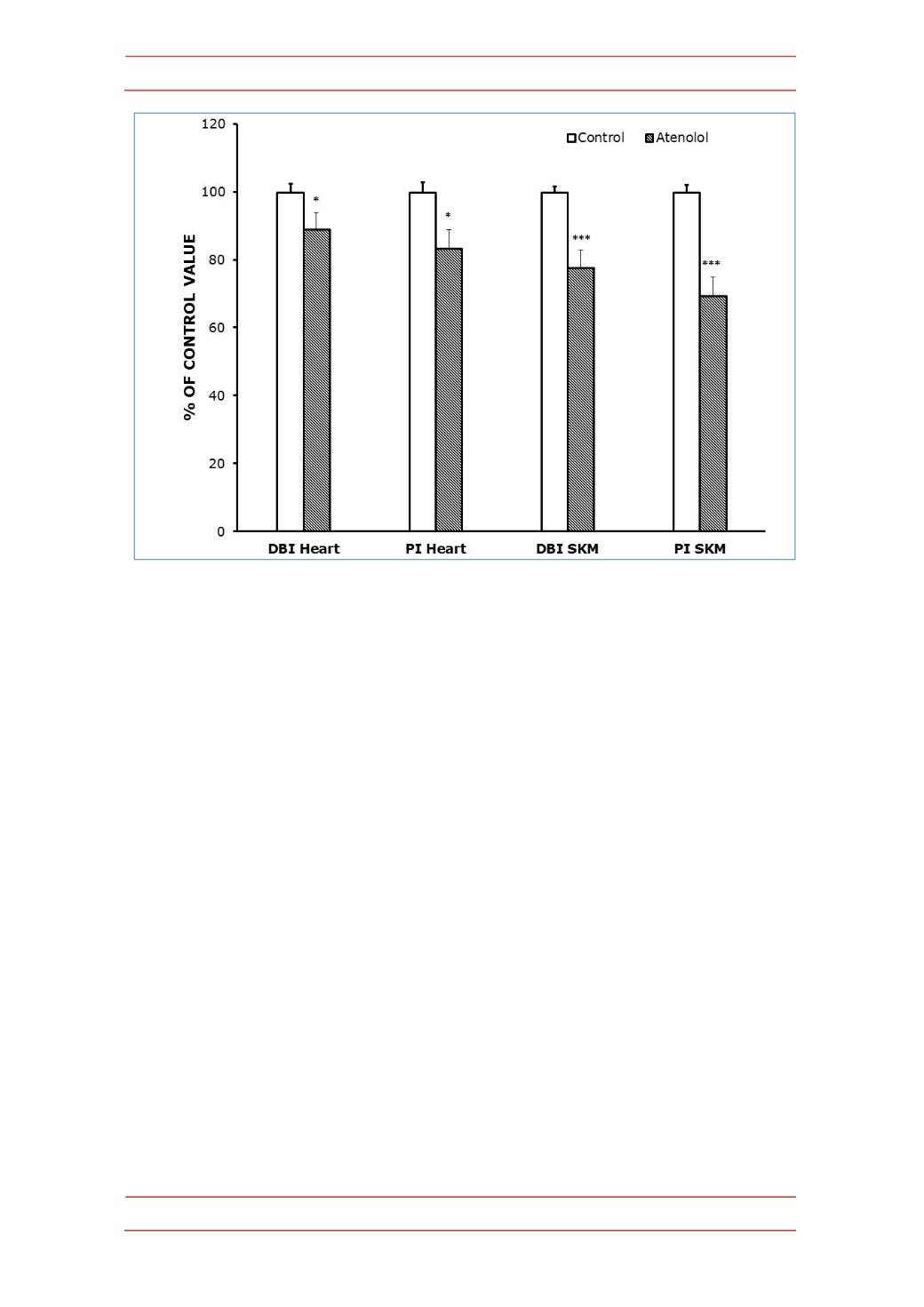
Figure 3.-‐
Double bond index (DBI) and peroxidizability index (PI) in heart (A) and SKM (B)
mitochondrial fatty acids from control and atenolol treated mice. Values are means ± SEM from 6
(heart) or 5-‐6 (SKM) different animals and are expressed as percentage of those in the controls for
each parameter. Control values: 232.60±5.90 (DBI, heart); 268.39±8.02 (PI, heart); 203.91±3.38
(DBI, SKM); 217.36±4.52 (PI, SKM). For calculation of DBI and PI values see the Materials and
Methods section. Asterisks represent significant differences between the control and the atenolol
group. * P<0.05; ** P<0.01; *** P<0.001.
Oxidative damage in heart mtDNA significantly decreased from 20.65±3.81 8-‐
oxodG/10
5
dG in Old Controls to 10.07±1.37 in Old AT (P<0.05), whereas in the case
of SKM the trend to decrease in the AT group did not reach statistical significance
(results not shown).
Protein oxidation, glycoxidation and lipoxidation markers are shown in
Figures 4 and 5. In heart mitochondria all the five markers measured, GSA, AASA,
CEL, CML and MDAL, were significantly lower in Old AT-‐animals than in Old controls
(Figure 4). In SKM mitochondria the values of GSA, AASA, CML and MDAL were
significantly lower in the atenolol treated animals. These decreases were rather
strong and ranged from 31% to 51% depending on the parameter measured and the
tissue considered. Only in the case of CEL the decrease shown by AT compared to
controls did not reach statistical significance (Figure 5). Concerning mitochondrial
biogenesis, antioxidant factors and signaling proteins, SIRT1 increased and Nrf2
decreased in Old AT in heart (P<0.05) but not in SKM mitochondria. TFAM decreased
in Old AT in SKM (P<0.05) but not in heart mitochondria, while PGC1 did not show
significant changes in any organ (results not shown). The ratio of the phosphorylated


